ARSA Survey – Industry Rebounds from Pandemic Into Market Questions
ARSA’s 2023 Member Survey, which is conducted during the first quarter of each year, found that the aviation maintenance industry rebounding from COVID business disruptions and anticipating growth despite global uncertainty.
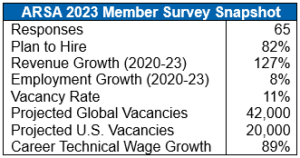
Respondents reported a 127 percent surge in revenue between 2020 and 2022. Large organizations – those with revenues of more than $1 billion –doubled revenues from pandemic lows. Overall, the median growth over the period was 26 percent, with only a minority of respondents lagging.
Not unexpectedly, the industry’s workforce is not growing at the same pace as business activity. Reported global employment increased eight percent since 2020; with U.S. firms’ workforces grew by 15 percent. This data reflects rebalancing by companies that were able, thanks to government intervention (for which ARSA was particularly vocal with American policymakers), to retain more personnel during the downturn.
The aerospace community continues to face challenges finding and retaining technical talent to sustain long term growth. Of the shared projections for market and hiring activities, the vast majority expect revenue growth (75 percent) and hiring (82 percent) in the coming year. Respondents also reported a vacancy rate of 11 percent in the industry’s overall workforce. Expanding this data across the international market’s nearly 400,000 maintenance employees, a shortage of approximately 42,000 individuals (20,000 in the United States) to meet current demand is projected.
New hires, once found, will enter a career in which wages nearly double between entry level and top end positions, with the highest-paying ARSA members reporting technical salaries exceeding $185,000 for full time employment.
As reported in ARSA’s Global Fleet & MRO Market Report, released by Oliver Wyman during the association’s 2023 Annual Conference, expectations of industry growth will face constraints. Survey respondents highlighted recruitment and global economic uncertainty as top challenges. Regulatory concerns, particularly related to maintenance instructions and supply chain impacts (e.g., parts documentation limitations), continue to plague and limited business opportunities.
ARSA remains popular with its most engaged members: Respondents rated the association 4.66 out of five in terms of satisfaction and most value access to its expertise and regulatory compliance support.
Previously from ARSA...
5/17/22 - ARSA Survey – Workforce Remains Top Concern
May 17, 2022
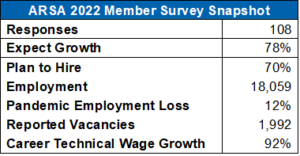 ARSA’s 2022 member survey paints a picture of an industry slowly recovering from the pandemic but still suffering a severe labor shortage. In total, 108 member companies from around the world responded to the survey.
ARSA’s 2022 member survey paints a picture of an industry slowly recovering from the pandemic but still suffering a severe labor shortage. In total, 108 member companies from around the world responded to the survey.
Members are generally optimistic about business conditions: 78 percent believe revenues and markets will grow, nine percent expect no change, eight percent expect contraction and five percent don’t know. Repair stations plan to hire: 70 percent intend to add workers in 2022, 21 percent expect no change in workforce, two percent plan to eliminate positions, and six percent do not know their company plans.
Hiring will be a challenge because the industry workforce still has not recovered from the pandemic. U.S. survey respondents reported having a total of 20,527 employees on Jan. 1, 2020 (before the pandemic), 16,181 as of Jan. 1, 2021 (a 21 percent year-over-year drop) and 18,059 on Jan. 1, 2022. Taken together, those numbers validate ARSA’s earlier findings about job losses during the pandemic and suggest the industry’s workforce is still 12 percent smaller than it was pre-COVID.
U.S. companies reported 1,992 vacant technical positions, representing 11 percent of the survey respondent workforce. Projected across the entire U.S. repair station industry (which employs 182,000 Americans), there may be as many as 20,000 vacant technician jobs nationwide.
Not surprisingly “difficulty finding/retaining technical talent” was identified as the most significant threat to the industry and their companies (cited by 72 percent of respondents). Other issues of concern include overall economic uncertainty (52 percent), maintenance information availability (42 percent), regulatory costs/burdens (28 percent) and inconsistent enforcement/interpretation of aviation rules (27 percent).
The survey found the average hourly entry-level wage for technical personnel at U.S. repair stations was $19.16 per hour. Technicians with five years’ experience earn $26.50 per hour on average and more experienced technicians at “the top end” earn an average of $36.72 per hour.
Sixty-two percent of U.S. respondents have at least one foreign civil aviation authority (CAA) approval and, on average, 34 percent of gross revenues are associated with foreign certificates. This underscores the risk to U.S. companies should foreign CAA’s retaliate against potential congressional action limiting the use of foreign repair stations.
Repair stations don’t operate in a vacuum; they’re an important part of the fabric of the U.S. economy. Respondents reported having an average of 25 certificated vendors (the median was 13); 25 uncertificated vendors supporting maintenance (median: 5) and 54 vendors supporting general business operations (median: 9).
Respondents also reported a high level of satisfaction with the association. On a five-point scale (with five being “very satisfied”) the average score was 4.55. Here are some of the open-ended comments we received about the association and the value of membership:
- “A voice to speak on behalf of all repair stations is priceless.”
- “Always very helpful when I have regulatory questions.”
- “ARSA is consistent. There is a lot of inconsistency elsewhere these days.
- “ARSA was very helpful with the pandemic explanation detail with money and working with the US to get funds.”
- “ARSA works on issues that benefit us as well as the entire industry. They understand (and communicate) that the things we need will take years to achieve. It’s all about keeping the pressure on and engaging the system on topics that can generate results for the membership.”
- “Gives us confidence and peace of mind to have ARSA’s knowledge and history of backing small business’s especially regarding regulatory guidance and enforcement.”
- “Good support when needed, a positive organization for the industry with training and advocacy.”
- “Great resource.”
- “ARSA has a dynamic group that keeps it entertaining.”
- “ARSA’s impact over the years has been excellent. The expertise on the regulations has been unparalleled.”
- “You guys are awesome!”
Respondents said the most valuable member benefits were access to ARSA’s expertise (regulatory/legislative questions): 4.59/5 (5 = very important), regulatory compliance support (4.57), congressional advocacy (4.34), free regulatory compliance resources (4.32); and the Dispatch and hotline newsletters (4.19).
The data provided supports ARSA advocacy on the industry’s behalf and ensures that association resources are properly allocated. Thanks to all members who took the time to participate.
5/4/21 - ARSA Survey – Recovery Renews Workforce Concerns
May 4, 2021
In the wake of 2020’s unprecedented economic disruptions, the aviation maintenance industry is showing signs of recovery. ARSA’s 2021 member survey illustrates cautious optimism tempered by renewed concerns about the technician shortage, which threatens to prevent companies from growing and seizing new opportunities in the next year.
One hundred sixteen U.S. companies representing 196 FAA-certificated repair stations in the United States responded to ARSA’s 2021 survey, which was conducted online in February and March 2021.
Total aggregate employment at companies responding to the survey was 22,952 workers on Jan. 1, 2020 and 19,360 workers as of Jan. 1, 2021, a 15.6 percent year-over-year drop. However, those numbers are better than the 25 percent year-over-year decline documented by ARSA last summer and 19 percent drop reported by members in October 2020. A majority of respondents (55.3 percent) expect their company’s revenues and markets to grow in 2021, with 25.2 percent expecting business activity to stay the same and just 6.8 percent anticipating contraction (roughly 12 percent were unsure what the future holds).
Without government assistance, the U.S. maintenance industry would be in much worse shape. More than half (56 percent) of respondents reported receiving forgivable Paycheck Protection Program loans, 14.6 percent received Small Business Administration Economic Injury Disaster Loans and 7.6 percent receive Air Carrier Payroll Support Program (“payroll support program” or PSP) grants. Maintenance companies received hundreds of millions of dollars in PSP support according to the U.S. Treasury Department.
With business picking up, repair stations are once again hiring. Well over half the survey respondents (59.2 percent) plan to add workers in 2021, 33 percent do not expect to change the size of their workforce and only a small sliver (1.9 percent) anticipate layoffs.
With so many companies on track to hire, the technician shortage has reemerged as a primary concern. More than half (52.5 percent) of survey respondents cited “difficulty finding/retaining technical talent” as a major strategic threat to their companies, second only to “overall economic uncertainty” (65.4 percent). Respondents reported 907 unfilled technical positions, representing 4.6 percent of the total reported Jan. 2021 workforce.
Other strategic challenges include regulatory costs/burdens (selected by 35.6 percent of respondents), inconsistent enforcement of FAA rules (27.7 percent), inconsistencies between national regulatory systems/duplicative oversight (22.8 percent), restrictions on international trade/markets (19.8 percent) and lack of access to capital for investment in facilities and equipment (5.9 percent).
The survey also highlighted the U.S. maintenance industry’s connections to both the global and local economies. More than three quarters (76.2 percent) of responding U.S. companies held at least one foreign maintenance approval in addition to their FAA repair station certificate. Those foreign approvals allow U.S. facilities to perform work on foreign aircraft and related components. On average, 31.3 percent of revenue is attributable to work under a foreign certificate, the survey found.
Repair stations also have strong connections to other businesses in their own communities. The median reported number of external vendors per respondent was 16: nine certificated and two non-certificated companies supporting maintenance activities and five companies supporting general business operations (e.g., janitorial services).
In addition to helping ensure the airworthiness of commercial and general aviation aircraft, U.S. repair stations are also essential to national security and public safety. Two thirds of respondents (66 percent) provide services to at least one government entity, with the military the largest customer (52.4 percent of respondents) followed by other federal departments or agencies (36.9 percent), state/provincial governments (21.4 percent) and local/municipal governments (14.6 percent).
While maintenance is the primary business activity of most ARSA members, aviation-related manufacturing is also an important revenue source. Close to one third of respondents (32 percent) hold FAA production approval, with 23.3 percent holding parts manufacturer approval, 15.5 percent holding a production certificate and 5.8 percent holding technical standard order authorization.
Respondents also evidence a high level of satisfaction with ARSA. On a scale of one to five, with five meaning “very satisfied”, the association received an average score of 4.58. The association’s most valuable services, according to respondents, are its regulatory compliance support (4.58 out five, with five meaning “very valuable”), access to regulatory/legislative expertise (4.53), free regulatory compliance resources (4.45), congressional advocacy (4.32), ARSA model manuals and supplements (4.16) and the Dispatch and hotline newsletters (4.14).
“Thanks to all the ARSA members who took the time to share their opinions and data in our most recent survey,” ARSA Executive Vice President Christian Klein said. “It’s been an unprecedented year for the maintenance industry, but with government assistance, our members have weathered the storm but now appear to be on a more positive economic trajectory. With the worst of the crisis behind us, ARSA looks forward to working with its members and industry partners to keep the recovery on track.”
5/14/19 - ARSA Finds Technician Shortage Costs Industry $100 Million Per Month
May 14, 2019
ARSA’s 2019 Member Survey paints a picture of a thriving, international industry whose growth and vitality are being threatened by a chronic shortage of technical workers.
Eighty-six companies, representing a diverse cross section of the industry and ARSA’s membership, responded to the annual data-gathering exercise. Repair stations come in all shapes and sizes, from small, highly-specialized component shops to large engine and airframe facilities with facilities spread across the world. Respondent reports of revenue reflect that diversity, ranging from less than $10 million in 2018 revenue to a slice of companies reporting well more than $1 billion.
Across this variety of businesses, with locations across the globe, a number of key trends emerged. Many of these perspectives are consistent with responses provided to each of ARSA’s recent member surveys:
Profitability Increasing, Markets Growing
ARSA members report that business activity is strong and they are confident about the future.
Supporting Global Customer Base
Nearly a quarter of respondents plan to seek new certifications from aviation authorities outside the United States in the next two years.
Government Business has Big Impact
More than half of respondents reported doing business with some federal, state or legal entity in the United States or overseas, including military contracts.
Technician Shortage is Biggest Concern, Costs Industry $1 Billion Per Year
 While the business forecast is good and industry leaders are generally optimistic, as reflected in past ARSA surveys, the technician shortage is a major concern.
While the business forecast is good and industry leaders are generally optimistic, as reflected in past ARSA surveys, the technician shortage is a major concern.
Underscoring the workforce challenge, more than two-thirds of U.S. companies reported vacant technician positions, a total of 4,615 openings. Those empty positions are having real consequences, increasing time to complete work, driving up overtime and training costs and preventing new business development.
Based on the survey data, ARSA projects the technician shortage is costing the U.S. aviation maintenance industry $118.416 million per month ($1.421 billion per year) in lost revenue. Those figures underscore the importance of ARSA’s work to attract, retain and train maintenance technicians. Among other things, the association is a leading a coalition to secure funding for the new technician workforce development grant program created at ARSA’s urging by the 2018 FAA reauthorization law and promoting repair station careers through its public relations and regulatory activities.
A full analysis of key survey response data will be made available for ARSA members in the May edition of the hotline newsletter. As always, the association’s advocacy teams will utilize data from the survey as necessary to support legislative and regulatory initiatives.
“Thanks to all the members across the U.S. and the world who took the time to respond to our 2019 survey,” ARSA Executive Vice President Christian A. Klein said. “The data our members provide helps us tell the industry’s story and ensure our priorities are aligned with member needs.”
4/24/18 - ARSA Survey Shows Industry Poised for Growth, Facing Technician Shortage Headwind
April 24, 2018
ARSA’s 2018 member survey, conducted during the first quarter of the year, paints a picture of a healthy and growing industry facing a major strategic threat in the form of a looming technician shortage.
Half of the 125 respondents reported increased profitability in the last two years (only 14 percent said profitability decreased) and two-thirds expect revenues and markets to grow in coming year (only two percent expect a decrease). Employment demand is also strong: 98 percent expect to add to or maintain the current size of their workforce, which will require hiring for new positions, filling vacancies or both. That may be more easily said than done given that 82 percent report difficulty finding qualified technical workers (37 percent report a lot of difficulty).
Survey respondents collectively reported more than 1,000 technician vacancies. Projecting this figure across ARSA’s entire membership means more than 2,500 unfilled technical positions. Using annual revenue data collected through the survey, ARSA estimates its members will forego between $333.5 million and $642.5 million in revenue this year if those vacant positions remain unfilled. Although ARSA represents a considerable number of repair stations, not all in the industry are association members. Thus, the actual potential economic impact of unfilled positions on the entire aviation maintenance industry is likely significantly higher.
ARSA has been asking questions about recruitment challenges for many years, but this was the first time the association polled its members about the practical effect of the skills gap. Eighty percent report the worker shortage increases time to complete work for customers, 28 percent have not added new capabilities, 20 percent have turned down work and 11 percent have decided against expanding facilities. Those results underscore how personnel issues ripple through the aviation industry and impact growth in communities around the country.
With the foregoing in mind, it is not surprising that difficulty finding/retaining technical talent was reported as the top strategic threat facing repair stations (53 percent of respondents). Other looming threats are availability of maintenance information (tied with workforce at 53 percent), regulatory costs/burdens (45 percent), inconsistencies between regulatory systems (28 percent) and restrictions on international trade/markets (18 percent).
The survey also underscores how important government business is for the aviation maintenance industry. Fifty-seven percent of respondents said their companies provide services to one or more governmental entities (whether in the United States or overseas). Forty-nine percent of respondents do business with the military, 17 percent work with some other part of the federal government, 13 percent work with state governments, and seven percent provide services to local governments.
Overall satisfaction with ARSA membership is also high (4.42 on average on a one to five scale on which five is “very satisfied”). Access to regulatory and legislative expertise was ranked as the most important member benefit (4.64 out of five). Other top-rated benefits include regulatory advocacy (4.55), free regulatory compliance resources (4.19), congressional advocacy (4.10), Dispatch and hotline newsletters (4.08) and ARSA online training (4.04).
The survey was conducted from January 23 to April 3. Multiple emails requesting participation were sent to the primary contact at each ARSA member company. One hundred and twenty-five ARSA member organizations responded, representing 488 U.S. and non-U.S. approved maintenance facilities. The survey’s estimated margin of error is seven percent (95 percent confidence level).
5/12/17 - Skills Gap Could Cost Repair Stations $1.95 Billion in Revenue, Survey Finds
May 12, 2017
ARSA members could miss out on close to $200 million in foregone revenues this year as a result of unfilled technical jobs at their companies, the association announced on May 12.
Fifty-five percent of respondents to ARSA’s recent member survey reported having unfilled positions. Based on the average number of vacancies at the responding organizations, the association estimates its members have 1,045 open technical jobs. The total economic loss figure – $185 million – was derived by multiplying the number of open positions by the $177,000 in average annual revenue per employee reported by respondents.
Projected across the entire population of FAA-certificated repair stations in the United States, the number of open positions may be close to 11,000. If those positions go unfilled, the industry could stand to miss out on as much as $1.95 billion in economic activity in 2017.
“These numbers are a snapshot of how just one industry is being affected by the technical worker shortage plaguing the U.S. economy,” ARSA Executive Vice President Christian Klein said. “Well-paying jobs in the high-tech aviation maintenance sector are going unfilled because workers aren’t available or candidates lack basics skills.
“We hope lawmakers working career technical education policy on Capitol Hill – including the recently-introduced Perkins reauthorization bill – will keep the aviation industry in mind when crafting solutions,” Klein said. “But Washington can’t solve this problem alone. Expanding the base of eligible job candidates and better aligning school curricula with repair station needs will require greater industry engagement at the local, state, and federal levels,” Klein said.
The worker shortage has become a major concern for maintenance providers. When asked to indicate the most-pressing risks to company business outlook, “difficulty finding and retaining technical talent” tied with “regulatory costs/burdens” among survey respondents. Availability of maintenance information, international regulatory inconsistencies and restrictions on trade rounded out the top five respondent concerns.
Despite these challenges, the survey found ARSA’s membership generally optimistic about the future. More than 90 percent of member companies expect their markets to expand or remain stable this year and more than half plan to add positions. The survey also underscored the significant impact that international business has on repair stations: almost one-third (31 percent) of revenues for the average U.S.-headquartered respondent came from customers outside North America.
ARSA Member Survey Respondent Overview
- Eighty ARSA member companies from around the world provided input for the survey, which was conducted during the first quarter of the calendar year.
- Respondents reported total 2016 gross annual revenues of $1.791 billion.
- Eighty-eight percent of respondents were headquartered in the United States.
- Respondents reported operating facilities in 29 of the 50 U.S. states.
- The best represented U.S. states were Florida (17 percent of respondents reported having facilities), California (17 percent), Texas (16 percent), Georgia (10 percent) and Ohio (10 percent).
If you have questions about the survey or the results, click here to contact ARSA.
To see more and learn about the international maintenance industry, visit the association’s Data & Advocacy page.
To see the other ways ARSA uses data to help inform its work, check out ARSA’s data and advocacy page.